Author: Ethan Getz, Marine Science Manager
January 2018
Over the past few months, the marine conservation staff have worked to continue long-term reef monitoring projects while developing new methods to measure the health of our home reef and the surrounding reefs on Nosy Komba. Robust datasets have been collected from reef transect surveys, turtle watch, and nudibranch surveys. These long-term surveys will provide valuable information on the health of our MPA and some of the indicator species that inhabit it. In the coming months, efforts will be made to analyze these data in depth to decipher developing trends. While long-term data collection from existing surveys remains the primary goal, staff have also recently developed new reef survey methods.
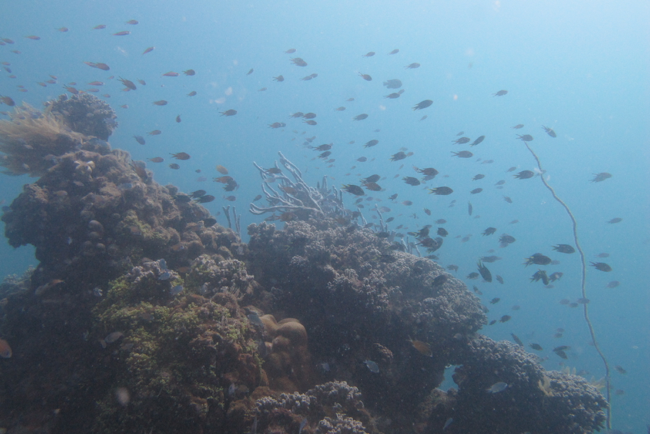
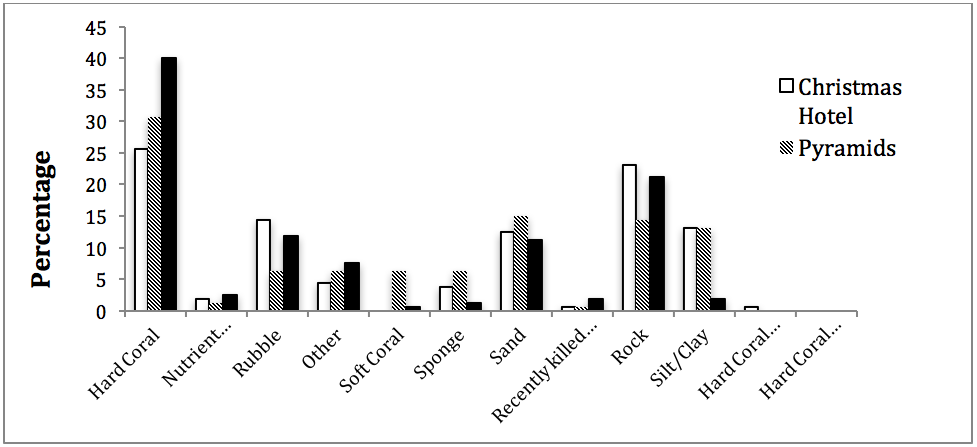
Baseline surveys using the Spirit of Malala were developed in November to assess the health of reefs all around Nosy Komba. To date, three baseline surveys have been conducted (at xmas tree hotel, greenhouse and pyramids) and data have now been analyzed. Results suggest that the south and west sides of Nosy Komba have healthy coral reefs while reefs are more sparse on the eastern side. Results from the sessile surveys indicate that no coral bleaching is currently happening and that the reef appears to be in a period of recovery. The presence of rock, sand and silt indicate that there have been damaging events in the past, but currently the reefs are rebuilding.
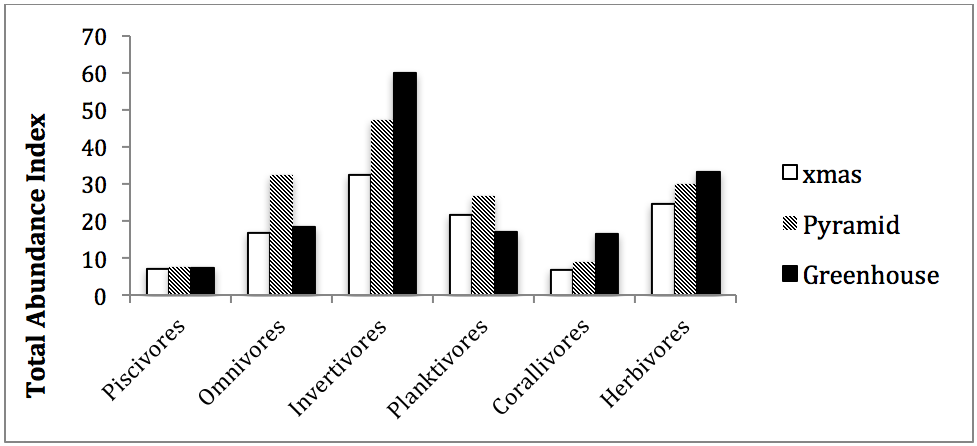
Active swimmer surveys were used to determine the number of fish species at each site and which functional group they belong to (i.e. piscivores, herbivores, ect.). Results suggest that there is a good distribution of fish from each functional group on each reef, but the relatively low abundance of piscivores indicates that overfishing may be a problem on Nosy Komba.
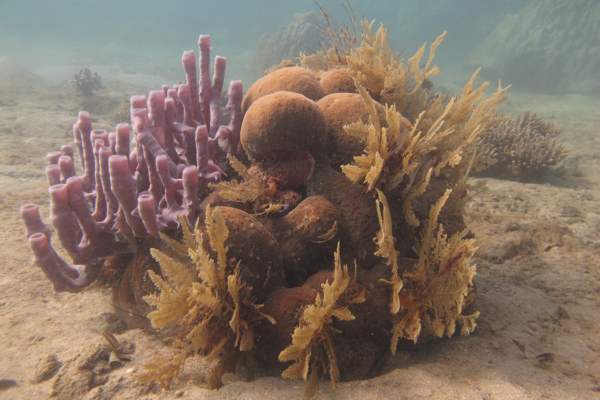
These species are generally the first ones to be fished out and their relatively low numbers point to fishing pressure in the area. Benthic surveys also provided data on invertebrate diversity around Nosy Komba and suggest that there is a healthy reef community.
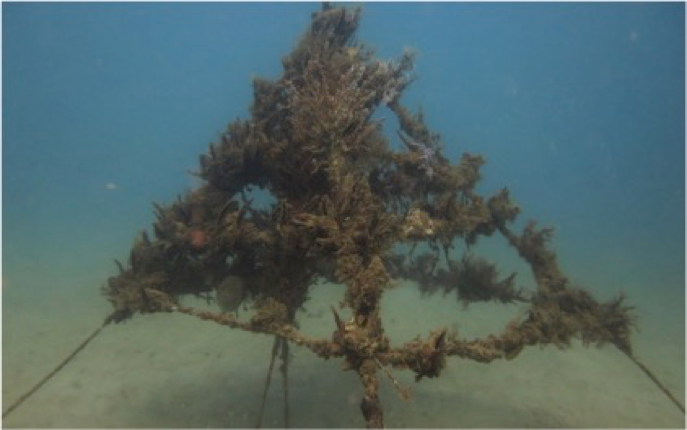
In addition to baseline surveys, artificial reef surveys on the pyramids at Stonehenge and Madhatter have produced meaningful data. On average, each pyramid provides habitat for 115 fish, 39 bivalves and a variety of sessile species. In addition, many species of fish such as the Malabar snapper and red emperor snapper are routinely found on the artificial structures, but only occasionally on the natural reef. The high abundance of juvenile fish on the pyramids is also an encouraging sign that the structures are acting as a nursery for fish larvae settling out of the water column. Overall, the pyramids seem to be increasing both abundance and diversity of many reef species making them well worth the investment to construct them.
Other ongoing projects include the coral bleaching surveys, invasive species surveys and turtle monitoring. Since coral bleaching and invasive species surveys have only just started, preliminary results will be analyzed in the coming months. Results from active turtle surveys, turtle walks and turtle watch are still being analyzed, but preliminary results suggest that there is a healthy population of resident turtles on our reef. Turtle walks have been less productive with only one hatched nest having been found, but it is clear that at least some turtles nest on Nosy Komba. In summary, the reefs around Nosy Komba appear to be showing the signs of human activities, but overall it is still a healthy reef system with strong community structure.
Find out more about our Marine Conservation Program Here